DNA Extraction Introduction – DNA extraction from blood/tissue/bacteria

DNA extraction is the process of extracting, isolating, and purifying DNA from the desired sample. We can do DNA extraction from blood, tissue, and also bacteria. Here we are going to discuss the protocol of DNA extraction from blood/tissue/bacteria. We will also describe DNA extraction by Kit method, organic and inorganic method, phenol chloroform-method, by the buffer, and by magnetic beads.
Table of Contents
Principle of DNA extraction:
Mainly the principle of DNA extraction is a disruption of the cell membrane, cell wall, and also nuclear membrane to release purified DNA into the solution which is followed by DNA precipitation and removal of contaminants for example polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and other metabolites. (DNA extraction from blood/tissue/bacteria)
DNA extraction from blood/tissue/bacteria
Extraction of DNA from the blood (Inorganic method):
Material required:
- TE buffer or lysis buffer
- TNE buffer and proteinase K
- 10 % SDS and 95 % ice cold ethanol
- PCI and DNase free water
Lab equipment required:
Pipettes, tips, racks, falcon tubes, 1.5ml sterilized microcentrifuge tubes, vortex, freezer, centrifuge machine
Blood sample:
Blood should be collected in an anticoagulant tube and samples should be stored in the freezer at 20 degrees centigrade prior to DNA extraction.
The stepwise procedure of DNA extraction from Blood
Lysis of RBCs or red blood cells:
- Here in this step, 800 microliter tris EDTA buffer is added in 200 microliters of blood and mixed well by inverting 10 times. EDTA is used to maintain the pH of a solution.
- Then after centrifugation at 5000 revolutions per minute for 10mins, discard the supernatant and break out the pellet by gently tapping it which is formed at the bottom of the tube.
- Then add 1 milliliter of TE buffer and gently mix it and again centrifuge it at the same revolution and time. We will repeat this step until the pellet color becomes light pink
Digestion or lysis of WBCs:
- Here in this step, there is a lysis of red blood cells which is done by adding 200 microliter SDS 10%, 400 microliter TNE buffer, and 50 microliter proteinase K. After this step, pellet is obtained. SDS is used for cell lysis in DNA extraction.
- Then with gentle rotation, we will homogenize the tube and incubate the sample overnight at 58 degrees centigrade in the shaker water bath.
Phase separation:
- In the phase separation step, protein is extracted. Here, we will add 6 molars of NaCl to remove digested protein. Then DNA is released into the solution. The purpose of salt in DNA extraction is that salt precipitates protein and release DNA in solution.
- Then remove carefully top aqueous phase containing DNA and move it in a separate tube.
Precipitation of DNA:
- Precipitation of DNA is done with absolute isopropanol and we have to gently invert the tube until threads of DNA become visible then left the tube for 10 mins at room temperature. We use ethanol for dna precipitation. We prefer ice cold ethanol for more precipitation of DNA.
- Then again centrifuge the tube and carefully discard the supernatant. After a while DNA pellet is visible at the bottom of the tube.
Washing of pellet with cold ethanol:
- Wash the pellet of DNA with 1 milliliter of 70% ethanol and break and mix the pellet gently and left for centrifugation for 10 mins at 8000rpm. Ethanol is used for the purpose of washing DNA.
- After centrifugation, discard the supernatant and air-dry the pellet at room temp.
Dilution of pellet:
- The last step of DNA extraction is the dilution step. Here 50-100 microliter of TE buffer is added and place the tube in a shaking water bath at 70 degree centigrade for 1 hour for inactivation of nucleases.
- Finally, store the DNA at -20 degrees centigrade.
DNA extraction from the blood (Organic method):
Extraction of DNA through organic method or Phenol–chloroform extraction is a liquid-liquid extraction method in molecular biology for purifying nucleic acids and removing proteins. (DNA extraction from blood/tissue/bacteria)
Material required for DNA extraction:
- TE buffer or lysis buffer
- TNE buffer and proteinase K
- 10 % SDS and 95 % ice-cold ethanol
- PCI and DNase free water
Lab equipment required:
Pipettes, tips, racks, falcon tubes, 1.5ml sterilized microcentrifuge tubes, vortex, freezer, centrifuge machine
Blood sample:
Blood should be collected in anticoagulant tube and samples should be stored in a freezer at 20 degree centigrade prior to DNA extraction.
The stepwise procedure of the Inorganic method
Lysis of RBCs or red blood cells:
- Here in this step, 800 microliter tris EDTA buffer is added in 200 microliters of blood. And mixed well by inverting 10 times.
- Then after centrifugation at 5000 revolutions per minute for 10mins. Discard the supernatant and break out the pellet by gently tapping it. Pellet is obtained at tube’s bottom.
- Then add 1 milliliter of TE buffer. And gently mix it and again centrifuge it at the same revolution and time. We will repeat this step until the pellet color become light pink
Digestion or lysis of WBCs:
- Here in this step, there is a lysis of red blood cells which is done by adding 200 microliter SDS 10%, 400 microliter TNE buffer, and 50 microliter proteinase K. After this step, the pellet is obtained.
- Then with gentle rotation, we will homogenize the tube and incubate the sample overnight at 58 degrees centigrade in a shaker water bath.
Phase separation:
- In phase separation step, protein is extracted. Here, we will add 6 molar phenol chloroform isoamyl alcohol. Then DNA is released into the solution and is extracted with phenol-chloroform isopropanol or PCI to remove proteinaceous materials. Phenol is used in DNA extraction to remove protein compounds.
- After adding the same volume of PCI and gently mix for 2 minutes and left for centrifugation at 10000rpm for 10 mins at 4 degree centigrade.
- Then remove carefully top aqueous phase containing DNA and move it in a separate tube.
Precipitation of DNA:
- Precipitation of DNA is done with absolute isopropanol and we have to gently invert the tube until threads of DNA become visible then left the tube for 10 mins at room temperature.
- Then again centrifuge the tube and carefully discard the supernatant. After a while DNA pellet is visible at the bottom of the tube.
Washing of pellet with cold ethanol:
- Wash the pellet of DNA with 1 milliliter of 70% ethanol and break and mix the pellet gently and left for centrifugation for 10 mins at 8000rpm.
- After centrifugation, discard the supernatant and air-dry the pellet at room temp.
Dilution of pellet:
- The last step of DNA extraction is the dilution step. Here 50-100 microliter of TE buffer is added and place the tube in a shaking water bath at 70 degrees centigrade for 1 hour for inactivation of nucleases.
- Finally, store the DNA at -20 degrees centigrade.
DNA extraction from tissue:

Material required for DNA extraction from tissue:
- Lysis mix
- RNase
- Charge switch purification buffer
- Chargeswitch magnetic beads
- Charge switch wash buffer
- Chargeswitch elusion buffer
- Storage buffer
Stepwise procedure for DNA extraction from tissue:
Preparation of tissue lysate:
- Firstly, put the sample into sterilized microcentrifuge tube and add 1 milliliter of lysis mix to it and make sure that there is the complete immersion of tissue in lysis buffer.
- After mixing with vortex, incubate the tube at 55 degrees centigrade overnight till the lysis is complete.
- Then add RNase A (5 micro liter) and make a homogeneous solution by pipetting up and down for five times and incubate for 5 mins at room temperature.
DNA binding step:
- In this step, DNA binds with the charge switch magnetic beads.
- Firstly, vortex the tube having ChargeSwitch magnetic beads to fully distribute and resuspend the beads in storage buffer and ensure all bead to settle at the tube’s bottom.
- Then add 200 microliters of charge switch purification buffer to the digested sample of tissue and mix gently by pipetting up and down.
- Then add 40 microliters of charge switch magnetic beads and gently mix it by pipetting up and down and incubate it for 1 min at room temperature to let the DNA bind with charge switch magnetic beads.
- Until the beads made a tight pellet, place the tube in magnaRack for 1 min. After gently remove the supernatant without removing a sample from MagnaRack.
DNA washing:
- Add 1 milliliter of Chargeswitch wash buffer to a tube having a pelleted magnetic beam without supernatant and resuspend the magnetic beads by pipetting up and down.
- Again, place the tube for 1 min in MagnaRack until beads made the tight pellet and remove the supernatant without removing the tube from MagnaRack and repeat the steps.
DNA elusion:
- Add 150 micro liter to chargeSwitch elution buffer to tube having pelleted magnetic beam without supernatant and resuspend the magnetic beads by pipetting up and down 10 times.
- Incubate it for 5 mins and again place the sample in MagnaRack until beads made tight pellet and remove the supernatant having DNA without removing the tube from MagnaRack and place it into the microcentrifuge tube
DNA storing:
- Use the DNA immediately for desired downstream application or stored at -20 degree centigrade for long-term use and 4-degree centigrade for short-term use. (DNA extraction from blood/tissue/bacteria)
Extraction of DNA from Bacteria
Material required:
- Detergent
- Cold alcohol
- coli solution
Step wise procedure to extract DNA from E. coli:
- First of all, write initials on the test tube containing detergent for identification and add the E. coli solution from the test tube into detergent tube.
- Then mix the solution by inverting it slowly and place it in the hot water bath for 10 mins at 55-60 degree centigrade and observe the alteration in the solution’s clarity.
- Heating and detergents will dissolve fats in the bacterial cell wall and frees the DNA.
- Then after removing the tube from the hot water bath, gently add cold alcohol in a test tube to make a layer of alcohol on the top of around 1 centimeter. The alcohol should be too cold for better results.
- We can add alcohol to a test tube through 3 ways
- By filling Pasteur pipette with cold alcohol and placing it to the bottom of the tube and gently release alcohol
- By slowly pouring cold alcohol with Pasteur pipette down inside the test tube
- And by putting 1 centimeter of cold alcohol down into the test tube and add sol.
- When we add alcohol then all the components present inside the test tube stays at the bottom except DNA as DNA is not soluble in alcohol. And the DNA is precipitated out in a layer of alcohol.
- After precipitation of DNA into alcohol layer, leave the sol. For 2-3 mins without any disturbance. Now we can easily see the white DNA in alcohol layer. This is how DNA is extracted from bacteria. (DNA extraction from blood/tissue/bacteria)
DNA extraction from the blood through the kit-based method:
Sample volume: 5-10 milli liter of fresh blood extract 30-100 microgram of DNA. The yield of DNA relies on the blood freshness as if blood has been stored for some days then yield will low.
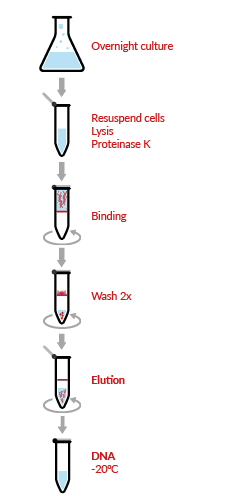
Stepwise procedure:
- First of all, add 40-45 ml of solution 1 which is prepared by mixing 15 milliliters of 3 times concentrate and 30 ml of ddH2O to the sample of blood in order to yield of 50 ml of the final volume.
- Then incubate it for 2 mins on ice.
- After incubation, spin the sample for 15 mins at 350*g (1500 revolution per minute by Beckman JS-5.2 rotor) at 4 degree centigrade.
- Then carefully discard the supernatant and save the gelatinous appearing pellet.
- After resuspending the pellet in 11 milliliters of solution 2, add pronase (for per ml sample use 0.44 microliter stock) to this suspension to produce 100 microgram/milli liter final concentration.
- Then incubate the sample with shaking at 37 degree centigrade for overnight or at for 1 hr. at 60 degree centigrade.
- After the process of incubation, add 4 milliliters of sol. 3 to tube and invert it several time for mixing and then place it on ice for 5 mins.
- In solution 3, the precipitates might be visible. These are normal and doesn’t affect DNA extraction.
How to Pellet the protein precipitates?
- For pelleting the protein precipitates, spin the tube for 15 mins at 2000*g (3400 revolutions per min by Beckman rotor) at 4 degrees centigrade.
- Then transfer the supernatant gently to sterile conical tube of 50 milliliters by using the large-bore pipette.
- In order to make 20 microgram per ml final conc. add RNase to the supernatant. And incubate it for 15 mins at 37 degrees centigrade.
- For DNA precipitation add 2 vol. of 100% ethanol in the supernatant and invert it gently until precipitation of DNA.
- By coiling with sterile glass rod, carefully remove the DNA. And then with 70% ethanol, rinse the DNA and dried it by slightly touching with Kimwipe.
- Then resuspend the DNA carefully in 500 micro liters of 10 millimolar Tris, and 0.1 milli molar EDTA buffer. and mix it by inverting the tube gently.
- Finally, store it at 4 degrees centigrade. (DNA extraction from blood/tissue/bacteria)
See also How many types of infection do we have?



