Why is Stem Cell Research Bad/Good – Disadvantages of Stem Cell Research

Stem cell research is a topic that has sparked a lot of debate and discussion. While some people believe it holds great promise for medical advancements, others have concerns about its ethical implications and potential drawbacks. In this article, we’ll explore why some people believe stem cell research is bad and the arguments they present.
Table of Contents
What is Stem Cell Research?
Before diving into the debate, let’s understand what stem cells are. Stem cells are special cells in our bodies that have the remarkable ability to develop into many different types of cells. They can repair damaged tissues and organs and have the potential to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries.
Why is Stem Cell Research Bad?
- Ethical Concerns: One of the main reasons why some people oppose stem cell research is because it often involves the use of human embryos. These embryos are typically obtained from fertility clinics and are destroyed in the process of harvesting stem cells. This raises ethical questions about the sanctity of human life and whether it is morally acceptable to destroy embryos for research purposes.
- Religious Beliefs: For many people, their opposition to stem cell research is rooted in their religious beliefs. Some religious groups believe that human life begins at conception, and therefore, the destruction of embryos is seen as morally wrong. They argue that all human life, even in its earliest stages, should be respected and protected.
- Concerns about Exploitation: Another concern raised by critics of stem cell research is the potential for exploitation. They worry that vulnerable populations, such as women donating eggs for research purposes or patients participating in clinical trials, may be taken advantage of or subjected to undue risks.
- Alternatives Exist: Some opponents of stem cell research argue that there are alternative methods available that do not involve the use of human embryos. For example, adult stem cells, which can be obtained from various tissues in the body, have shown promise in medical treatments without the ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cells.
While stem cell research holds great promise for medical advancements, it also raises important ethical and moral questions. The debate surrounding this topic is complex, with valid arguments on both sides. It’s essential to consider the ethical implications carefully and weigh the potential benefits against the concerns raised by critics. Ultimately, finding a balance between scientific progress and ethical considerations is crucial in navigating the future of stem cell research.
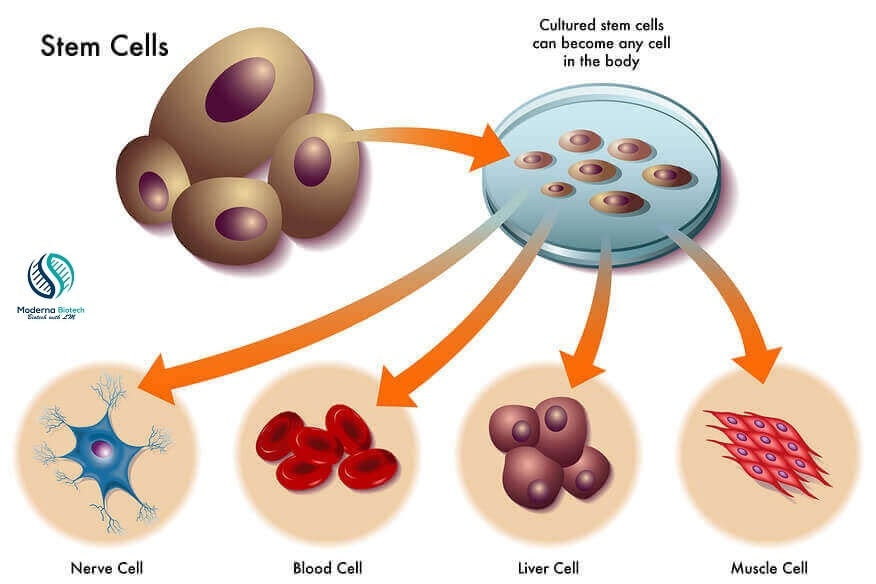
Disadvantages of Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research has gained attention for its potential to revolutionize medicine, but it’s important to also consider its disadvantages. In this article, we’ll explore some of the drawbacks associated with stem cell research in simple terms.
- Ethical Concerns: Stem cell research often involves the use of human embryos, which raises ethical questions. Some people believe it’s wrong to destroy embryos for research purposes, as they consider it the beginning of human life. This debate over the moral implications of stem cell research is ongoing and can’t be overlooked.
- Risk of Rejection: While stem cells hold promise for treating various diseases and injuries, there’s a risk of rejection by the recipient’s immune system. This means that even if stem cell treatments are successful in the lab, they may not work as effectively in real-life scenarios. Finding ways to minimize this risk is a significant challenge for researchers.
- Potential for Tumor Formation: Another concern with stem cell therapies is the potential for tumor formation. When stem cells are transplanted into the body, there’s a risk that they could grow uncontrollably and form tumors. Researchers need to carefully monitor this risk and develop strategies to prevent it from happening.
- High Cost: Stem cell research and therapies can be expensive, making them inaccessible to many people. The high cost of stem cell treatments can create disparities in healthcare access, with only those who can afford it benefiting from these advancements. This raises important questions about equity and fairness in healthcare.
- Regulatory Challenges: Stem cell research is subject to strict regulations and oversight due to its sensitive nature. Navigating these regulatory hurdles can be time-consuming and costly for researchers, slowing down the pace of progress in the field. Balancing the need for safety with the desire for innovation is a constant challenge.
- Limited Understanding: Despite significant progress, scientists still have much to learn about stem cells. The complexities of how stem cells function and interact within the body remain largely unknown. This lack of understanding poses challenges for researchers in harnessing the full potential of stem cell therapies.
- Risk of Genetic Abnormalities: During the process of culturing and manipulating stem cells in the lab, there’s a risk of inducing genetic abnormalities. These abnormalities could potentially lead to unintended consequences, such as the development of genetic disorders or other health complications in patients receiving stem cell treatments.
- Ethical Considerations Beyond Embryonic Stem Cells: While much attention is focused on the ethical concerns surrounding the use of human embryos in stem cell research, other ethical dilemmas exist. For example, the sourcing of adult stem cells from donors raises questions about informed consent, privacy, and potential exploitation. Ensuring ethical practices across all aspects of stem cell research is paramount.
- Long-term Safety Unknown: The long-term safety of stem cell therapies remains uncertain. Since many stem cell treatments are still in experimental stages, their effects on patients over extended periods are not fully understood. Monitoring patients for potential adverse effects and ensuring the safety of stem cell-based interventions is crucial.
- Risk of Commercialization: As stem cell research progresses, there’s a risk of commercial interests overshadowing scientific integrity and patient welfare. Profit-driven motives could lead to the premature introduction of stem cell therapies into the market without adequate testing or consideration of long-term consequences. Safeguarding against unethical commercialization is essential.
While stem cell research offers hope for treating various diseases and injuries, it also comes with its share of disadvantages. From ethical concerns to practical challenges like rejection and tumor formation, there are important considerations to weigh. By addressing these drawbacks and finding solutions, researchers can continue to advance stem cell therapies in a responsible and ethical manner.
Why is Stem Cell Research Good?
Stem cell research is a field of science that offers hope for improving human health in many ways. Let’s explore some of the reasons why stem cell research is considered valuable and beneficial in easy-to-understand terms.
- Potential for Treating Diseases: Stem cells have the amazing ability to develop into different types of cells in the body. This versatility means they can potentially be used to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries, such as diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and heart disease. Scientists believe that harnessing the power of stem cells could lead to revolutionary treatments that improve the lives of millions of people.
- Regenerative Medicine: One of the most exciting applications of stem cell research is in regenerative medicine. Stem cells can help repair damaged tissues and organs by replacing or regenerating diseased cells. This could mean new treatments for conditions that currently have limited options, such as repairing damaged heart tissue after a heart attack or restoring mobility in patients with spinal cord injuries.
- Better Understanding of Development and Disease: Studying stem cells gives scientists valuable insights into how the human body develops and functions. By understanding the processes involved in cell growth and differentiation, researchers can learn more about the underlying causes of diseases and develop more effective treatments. This knowledge could lead to earlier diagnosis, better prevention strategies, and improved outcomes for patients.
- Drug Testing and Development: Stem cells can also be used as a tool for testing new drugs and therapies. By growing stem cells in the lab and exposing them to different substances, scientists can assess how drugs affect specific cell types and predict their potential effectiveness and side effects. This can streamline the drug development process, making it faster, more efficient, and safer for patients.
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in stem cell research have paved the way for personalized medicine approaches. By using a patient’s own stem cells, doctors can create tailored treatments that are specifically matched to their unique genetic makeup and medical history. This personalized approach has the potential to improve treatment outcomes and minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
Stem cell research holds tremendous promise for revolutionizing medicine and improving human health. From treating diseases and injuries to advancing our understanding of development and disease, the potential benefits are vast. By continuing to support and invest in stem cell research, we can unlock new possibilities for medical advancements that benefit individuals and society as a whole. See Also Interesting facts about Stem cells – Uncovering Truths

Advantages of Stem Cell Research
Stem cell research is a fascinating area of science with many potential advantages for improving human health. Let’s take a closer look at some of the reasons why stem cell research is considered valuable and beneficial, explained in easy-to-understand terms.
- Treatment of Diseases: Stem cells have the remarkable ability to develop into various types of cells in the body. This unique characteristic holds promise for treating a wide range of diseases and medical conditions. Stem cell therapies could potentially help individuals with conditions such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and even certain types of cancer. By replacing damaged or malfunctioning cells with healthy ones, stem cell treatments may offer hope for improved health and quality of life for many people.
- Regeneration of Tissues and Organs: Another exciting aspect of stem cell research is its potential for regenerative medicine. Stem cells can regenerate and repair damaged tissues and organs in the body. This capability opens up possibilities for treatments that could help individuals recover from injuries or diseases that currently have limited treatment options. For example, stem cell-based therapies could aid in regenerating heart muscle tissue after a heart attack or repairing spinal cord damage caused by injury.
- Understanding Development and Disease: Studying stem cells provides valuable insights into how the human body develops and functions. By observing how stem cells grow and differentiate into specialized cell types, scientists can better understand the underlying mechanisms of various diseases and disorders. This knowledge helps researchers identify potential targets for new treatments and develop more effective therapies. Additionally, studying stem cells can lead to advances in areas such as developmental biology and tissue engineering, further expanding our understanding of human health and disease.
- Drug Testing and Screening: Stem cells are also used in drug testing and screening processes. By growing stem cells in the laboratory and exposing them to different drugs and compounds, researchers can assess their effectiveness and safety. This approach allows for more accurate predictions of how drugs will behave in the human body, potentially leading to the development of safer and more efficient treatments. Stem cell-based models offer a valuable tool for pharmaceutical companies to test new drugs and identify potential candidates for further development.
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in stem cell research have the potential to revolutionize personalized medicine. By using a patient’s own stem cells, doctors can develop customized treatments tailored to the individual’s specific needs and genetic makeup. This personalized approach holds promise for improving treatment outcomes and reducing the risk of adverse reactions. Additionally, stem cell-based therapies may offer new options for patients who do not respond well to traditional treatments or who have limited treatment options available.
Why is Stem Cell Research Controversial?
Pros & Cons of Stem Cell Research:
Pros of Stem Cell Research:
- Potential to treat a wide range of diseases and medical conditions.
- Ability to regenerate damaged tissues and organs.
- Enhanced understanding of human development and disease mechanisms.
- Improved drug testing and screening processes.
- Opportunity for personalized medicine approaches.
- Potential to revolutionize medical treatments and improve patient outcomes.
- Advancement of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering technologies.
- Potential to reduce healthcare costs in the long term by providing more effective treatments.
- Opportunity for scientific and technological innovation in the field of biomedicine.
Cons of Stem Cell Research:
- Ethical concerns regarding the use of human embryos in research.
- Risk of genetic abnormalities and tumor formation in stem cell therapies.
- High cost associated with stem cell research and treatments.
- Regulatory challenges and oversight requirements.
- Uncertainty about long-term safety and efficacy of stem cell therapies.
- Potential for commercialization and exploitation of vulnerable populations.
- Limited public understanding and awareness of stem cell research.
- Religious and cultural objections to certain aspects of stem cell research.
- Concerns about equitable access to stem cell treatments across different populations.
- Complexity of stem cell research requires significant investment in training and infrastructure.