What immunological techniques are used in the detection of infection?

Actually, Protein biomarkers are sensitive in detection as they can identify as well as quantify proteins in complex biological samples to diagnose a specific type of disease. In this article, we are going to discuss what immunological techniques are used in the detection of infection. We will also find out which immunological approaches are used to detect protein biomarkers of disease.
What immunological techniques are used in the detection of infection?
The immunological technique which is used to detect infection or Protein Biomarkers of Disease:
Immunological approaches are very helpful in the identification of protein biomarkers because they show sensitivity, specificity, as well as have simplicity for diagnostic assays.
- Agglutination
- ELISA
- Immunoassays
- Protein microarrays
- Immunohistochemistry
- Western blot etc.
Agglutination: –
- Actually, these are simple, inexpensive, rapid, and highly specific immunological tests.
- Firstly, they are used for human blood typing based on the presence of specific antigens on the surface of RBCs.
- ABO blood group tests are performed using antiserum which contains antibodies against either A or B surface antigen that are present in the patient blood.
- Antiserum mix with the drop of blood sample then if agglutination occurs then it indicates the specific blood type of that patient.
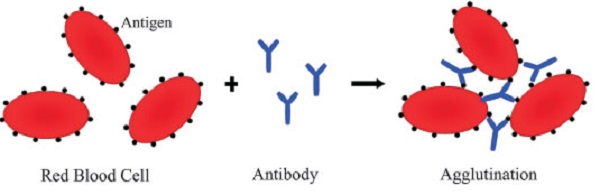
Type A blood:
Individual produces A antigen which agglutinates with anti-A antiserum but not with anti-B antiserum.
Blood type B:
An individual produces B antigen which agglutinates with anti-B antiserum but not with anti-A antiserum.
Type AB blood:
An individual produces both A and B antigens with antiserum.
Blood type O:
Individual produces no antigen so, no agglutination
ELISA: –
- Actually, ELISA stands for Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- Firstly, this diagnostic method used for quantitative and qualitative identification of a large variety of proteins related to the disease.
- Secondly, it measures antigen or antibody produced against an antigen in a sample
- Based upon affinity binding between antigen and antibody
- Detection depends upon the activity of the enzyme bonded to the antigen.
- g. Diagnosis of autoimmune diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
Types of ELISA: –
- Direct ELISA
- Indirect ELISA
- Sandwich ELISA
- Competitive ELISA
Direct ELISA: –
- Only one antibody is used
- Fast and simple
- Sample or an antigen is immobilized directly on the plate and a conjugated detection antibody binds to that target protein
- The substrate is then added which produces a signal that is proportional to the amount of protein in the sample
Indirect ELISA: –
- Like direct ELISA but uses two antibodies.
- An unconjugated primary detection antibody is added and binds to the specific antigen
- Then, a conjugated secondary antibody directed against the host species of the primary antibody is added.
- The substrate then produces a signal proportional to the amount of antigen bound in the well.
- Identifies immune response to show protein or pathogen
- High sensitivity
- Finally, Results are determined by a color change
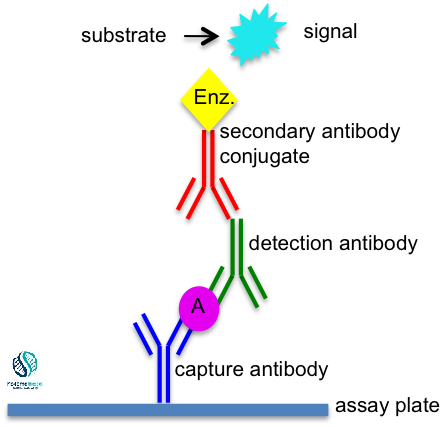
Sandwich ELISA:-
- Actually, it uses one monoclonal technique
- Identifies antigens between the two layers of antibodies
- The capture antibody is coated on a microplate then the sample is added and the protein of interest binds and is immobilized on the plate.
- Here, A conjugated antibody is then added and binds to an additional epitope on the target protein
- The substrate is added and produces a signal that is proportional to the amount of protein present in the sample
- Mainly, it highly specific
Competitive ELISA:-
- Primarily, it is based on the competitive binding
- Secondly, it quantitates small molecules
- Here, A conjugated antigen is used to compete for binding with the antigen present in the sample to capture the antibody.
- The substrate is added and the signal produced is inversely proportional to the amount of protein present in the sample
- It is actually less specific
Immunoassays: –
Immunoassay for Detection of infectious agent:-
- Primarily, it detects infectious disease
- Secondly, it targets proteins produced by a pathogen
- Thirdly, it detects the presence of antibodies produced against the pathogen
- Fourthly, it is Based upon the physiological or biochemical activity of microbe
- Fifthly, The translated protein of microbe can also be used for diagnosis
- Finally, Detection is done before a blood transfusion to prevent Hepatitis transmission
Immunoassay for Conformation of specific disease:-
- Here there is protein aggregation and cell death because of protein misfolding
- Development of antibodies to differentiate between two conformations
Protein microarrays:-
- Actually, it detects polygenic disease
- Affinity binding of antibody in the array with antigen to identify an infectious agent
- Used to detect allergies
- For example, diagnosis of autoimmune disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, pemphigus Vulgaris
Immunohistochemistry:-
- Actually, it identifies immune antigens
- Based on antigen-antibody reaction
- For example, Diagnosis of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
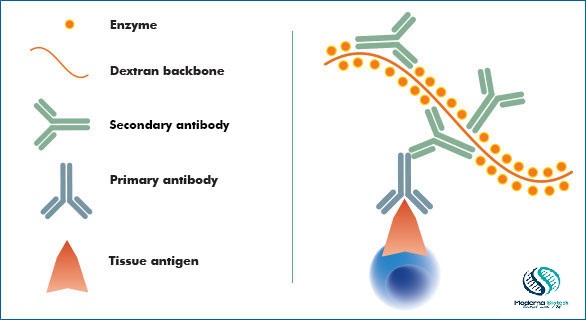
Types:-
- Direct IHC
- Indirect IHC
Direct IHC:-
- Here, Antigen-antibody is combining with a fluorochrome
- Enzyme introduction and detection of visual signal
Indirect IHC:-
- An antigen-primary antibody, non-conjugated-secondary antibody are combined with a fluorochrome or an enzyme
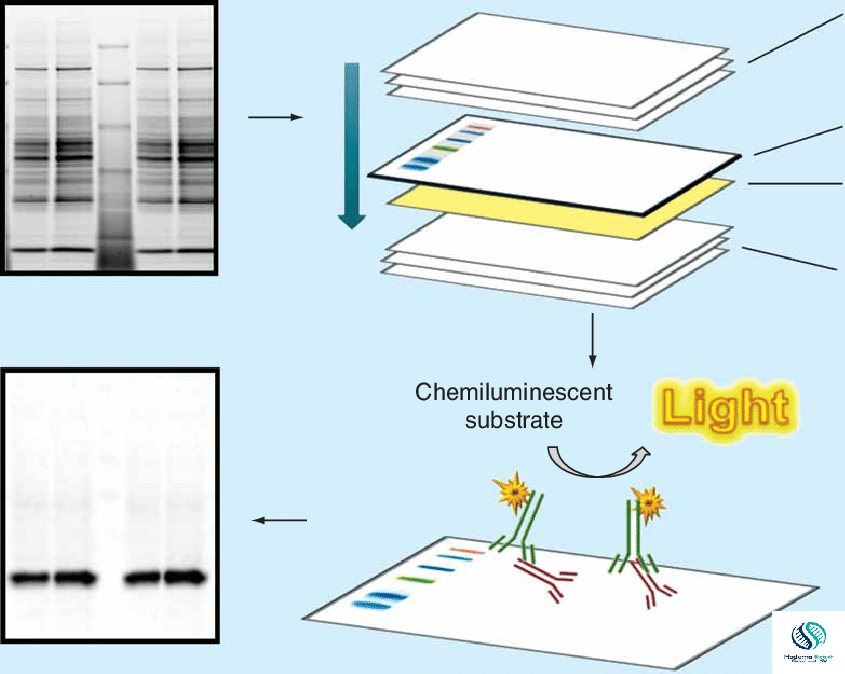
Western blot:-
- Here, there is an Identification of specific protein from a sample
- Electrophoretic gel analysis
- Transfer to nitrocellulose membrane
- Identification through labeled antibody
- For example, diagnosis of HIV and some autoimmune diseases, Sjogren’s syndrome.
This is the answer to the question, What immunological techniques are used in the detection of infection?
==============================================================
Read also Genome structure and pathogenesis of covid-19