Types of fermentation on the basis of product

Fermentation is a metabolic process where a complex substance breaks down into simpler substances. Fermentation has countless benefits in food production, laboratory scale as well as in industrial scale. Here you will know about the types of fermentation on the basis of product.
Table of Contents
What is fermentation
A metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates the action of enzymes is known as fermentation. Fermentation is also defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen.
Fermentation lets the preservation of considerable amounts of food through alcohol, acetic acid, lactic acid, and alkaline fermentations.
Types of fermentation on the basis of product
Based on the product, fermentation could be classified on the basis of the product used. There are numerous types of fermentation-based products. A few of them are as follows;
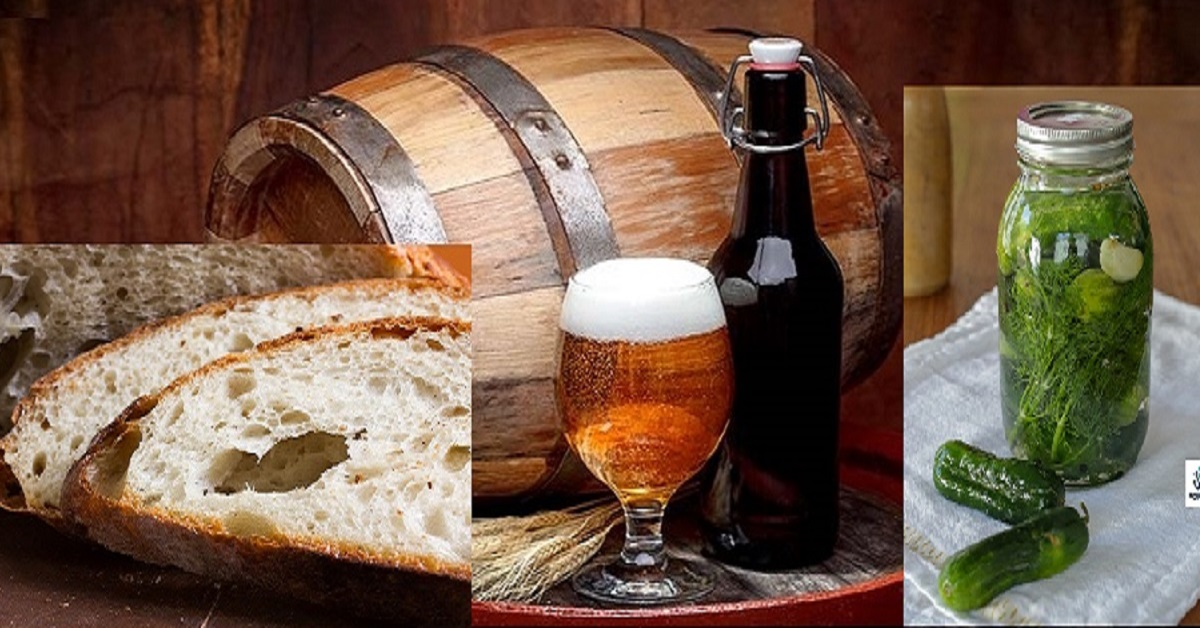
Beer fermentation:

- Beer fermentation is a type of fermentation wherein the wort, the yeast converts the glucose into carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol while giving the beer both its contended alcohol and carbonation.
- When beer fermentation is about to complete, much quantity of yeast will settle down to the bottom of the fermenter.
- The lower part of the fermenter is cone-shaped. This cone shape makes it easy to capture and take away yeast, which is used and saved for the subsequent batch of beer.
- The beer is cooled to 32 degrees Fahrenheit when the process of fermentation is complete. This will make the remaining yeast and undesirable protein settle at the bottom of the fermenter.
- Now the beer is slowly pumped and filtered to remove the remaining undesirable solid and goes into another tank known as bright beer tank.
- Here the CO2 level is adjusted by bubbling a little extra carbon dioxide by porous stone. And the last step is kegging and bottling.
Citric acid fermentation:
- Citric acid is generally the most significant organic acid produced which is widely used in pharmaceutical industries.
- It is chiefly produced by submerged fermentation using Aspergillus niger from different carbohydrate sources for example starch based media and molasses.
- There are also some alternative techniques for citric acid production such as surface fermentation and solid-state fermentation.
- For the production of citric acid, a huge number of bacteria comprising yeast, bacteria, and fungi have been employed.
- Under drastic imbalance conditions, citric acid is considered as a metabolite of energy metabolism and its accumulation increases the inconsiderable amount.
Pickle fermentation:

- For making pickle products, we generally use lactic acid fermentation.
- Lactic acid fermentation depends on valuable culture to break down normal sugars into vegetables and made variability of healthy substances chiefly lactic acid.
- The process of fermentation initiates with nutrient-rich and fresh vegetables, the cultures of naturally bearing lactic acid on their surfaces.
- The product is mixed with salt after washing, chopping, and slicing as per requirement.
- The salt was added to preserve the vegetables, draw out juices while starting, and regulating the process of fermentation.
- Then the mixture is packed into fermentation vessels which are airtight and placed in a spot that was warm.
- Pickles of cucumbers undergo considerably short fermentation on the other hand cabbages’ pickles could many months to produce sauerkraut.
- It is worth note that lactic acid is chiefly accountable for preserving vegetables along with creating a pleasing aroma and flavor of a traditional pickle.
Bread fermentation:

- During bread fermentation, yeast converts sugar which is present in flour into ethyl alcohol and CO2.
- Carbon dioxide gas is then trapped through gluten protein present in flour which makes the dough rise.
- Saccharomyces Cerevisiae is employed in bread making and it is used for the act of fermentation to convert sugar into CO2 and alcohol.
- CO2 makes the bread soft and fluffy after it is cooked and causes the dough to rise.