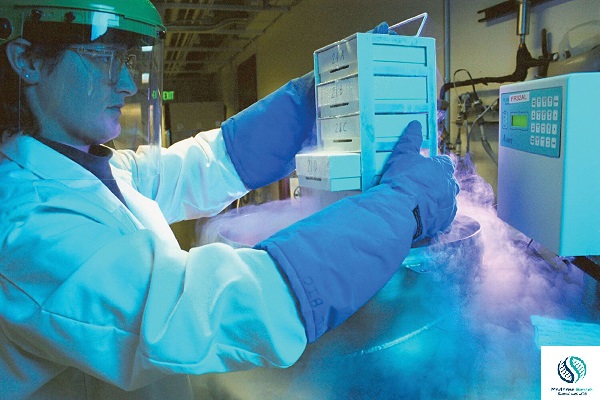
How cryopreservation is done? | Mechanism
What is Cryopreservation?
Cryopreservation meaning:
Cryo is derived from the Greek word which means frost. Cryopreservation generally means preservation in a “frozen state.” Cryopreservation is a procedure that is used to store many organelles, extracellular matrix, tissues, organs, or cells at a very low temperature of about -196⁰C to prevent it to damage by the extracellular environment. We use the temperature of the cryopreservation very low because it causes zero metabolisms of the cell and there is no chemical reaction take place. A cryoprotectant is generally a substance that is used to protect biological tissue from freezing damage. Cryoprotectants are typically antifreeze compounds. Here, we are going to discuss how cryopreservation is done.
Table of Contents

Examples of cryopreservation:
- Eggs in oocyte cryopreservation
- Semen in semen cryopreservation
- Blood
- Tissue sections like tumors
- Umbilical cord blood and many more
How cryopreservation is done?
Mechanism:
- In the first step, we should check properly our cell culture which we have to be preserved that no contamination is present. If contamination is present, then we have to destroy the frozen material.
- Now, for the cryopreservation, we should prepare the freezing medium by adding 5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). We should not add undiluted DMSO to a cell suspension, so to dilute the DMSO, add some distilled water.
- Then accumulate some cells by moderate centrifugation and put them back in the suspension of freeze medium at 1×106to 5×106viable cells/mL concentration.
- Now label the vials with the date and time and then add 1 to 1.8 mL of the cell deferment to each of the vials and close them.
- In the next step, the collected cell permit equilibrating in the freezing medium at 25⁰C for 15 to 20 minutes. After 40 minutes due to the presence of DMSO, cell viability may decline.
- Then in the next step, put the vials into a controlled-rate freeze and pre-cooled (at about 4°C) chamber and put this chamber in an automatic freezer for 24 hours at about -70°C temperature.
- Then instantly place the vials to liquid nitrogen or -130°C freezer.
- After 24 hours, remove one vial at -130°C, re-establish the cells in the culture medium, and find out their feasibility and infertility.
- Note the locality and all the details of the freeze.

Why cryopreservation is done?
Cryopreservation is used for the storage and freezing of hematopoietic stem cells. These stem cells are found in the peripheral blood and bone marrow.
One of the important applications of cryopreservation is the freezing and storage of human sperms and embryos.
It is a valuable technique for freezing extra embryos that are produced by in vitro fertilization.
Couples could choose this extra embryo for later pregnancies. Or they can use it in the event when IVF fails with fresh embryos.
In the course of the transfer of the frozen embryo, the embryos are thawed and set in into the woman’s uterus. Frozen embryo transfer is linked with a small but substantial increase in the risk of childhood cancer among children born from those embryos.
Methods of cryopreservation:
There are the following methods which are used for freezing:
- Slow freezing method
- Rapid freezing method
- Dry freezing method
Risk factors:
- This technique is very expensive.
- During the procedure, ice formation can result in needle-shaped crystals which may result in damage to the cell membrane.
- In this technique, there is an unequal distribution of cryoprotectants.
- Due to the migration of water from the material cell become dehydrate so it can directly harm the cell.
See also How are biosensors useful to us?