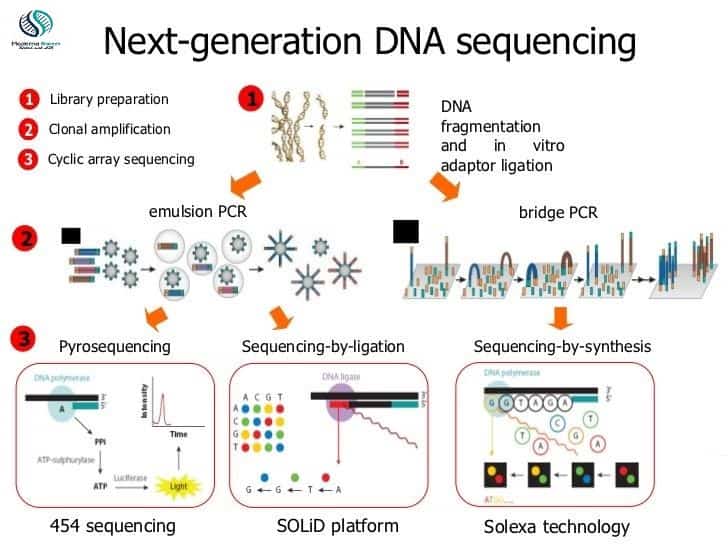
Next-generation sequencing steps
NGS technology
Principle:
The principle of NGS or next-generation sequencing is quite similar to the Sanger sequencing technique which relies on capillary electrophoresis. The genomic strand is fragmented and each base in respective fragments is recognized by emitted signals when fragments ligated contrary to the template strand. (Next-generation sequencing steps)
Material required:
- Adaptor
- Emulsion oil
- Thermal cycler
- DNA polymerase
- DNA ligase
- Primer
Next-generation sequencing steps
1- Library preparation:
First of all, DNA is fragmented either enzymatically or through sonication to make smaller strands. Adopters are short double-stranded synthetic DNA pieces that are then ligated to these smaller fragments with DNA ligase enzyme help which can combine the DNA strands. Adaptors are synthesized so that’s why one end is sticky and another one will be blunt which shows the joining of the blunt end to the blunt-ended DNA. This could lead to the potential base-pairing problem among molecules and so dimer made. To stop this chemical structure of DNA is used since ligation takes place between two ends. by removing the phosphate group from the adaptor’s sticky end and making 5′-OH end in leu the DNA ligase unable to make a bridge between two termini.
2- Amplification
Library amplification is needed so that the received signal from the sequencer is strong enough to detect accurately. There are many different types of amplification processes that use PCR to create DNA large cluster numbers.
Emulsion PCR
Emulsion oil beads PCR mixed and library DNA mixed to make emulsion leads to the microwells formation. The PCR denatures library fragment leading to two separate strands each anneal to the bead and it will be amplified by polymerase starts toward bead from primer site. Then reverse strand denature from bead to reanneal which gives two strands. the process is repeated over 30-60 cycles to make DNA clusters.
Bridge PCR
Flow surface of cell densely coated with comp[lementary primers for attached primers of DNA library fragments. Randomly DNA attached to the cell’s surface and exposed to the reagents for a polymerase-based extension. Due to nucleotide and enzyme addition free ends of single-stranded DNA attached themselves to the cell surface through complementary primers making bridge structures. enzymes interact with bridges to make them double stranded when denaturation occurs two ssDNA fragments attached to the surface in close proximity leads to the clonal clusters of localized identical strands
3- Sequencing
Several competing methods of next-generation sequencing have been created by various companies.
454 pyrosequencing
It is based on the principle of synthesis sequencing wherein a complementary strand is usually synthesized in polymerase enzyme presence in contrast to using dideoxynucleotides to dismiss chain amplification
Iron torrent Semiconductor sequencing
It uses a synthesis sequencing approach in which a new DNA strand complementary to the target strand is synthesized one base at a time. Semiconductor chip detects hydrogen ions made during DNA polymerization.
SOLiD (Sequencing by ligation)
It is an enzymatic sequencing method that uses DNA ligase enzyme and it is widely used in biotechnology due to its ability to ligation of double-stranded DNA strands. emulsion PCR used to immobilize or amplify the adaptor which has been conjugated to the target sequence on the bead. These beads then transferred to glass. In the glass, the high surface density of beads achieved which in turn increases the technique’s throughput.
Illumina (reversible terminator sequencing)
It differs from the traditional sanger process. Instead of terminating primer extension irreversibly using dideoxynucleotide is used in reversible termination. whilst many other techniques use emulsion PCR to amplify DNA library fragments reversible termination uses bridge PCR improved the efficiency of this method’s stage.
Result and its interpretation:
DNA fragmentation and adaptor ligation gives DNA colonies and also provides information about many DNA sequences in genetic disease treatment, in biological research studies, etc.
Uses:
- In whole-genome sequencing
- In the investigation of genomic diversity
- It has metagenomic approaches
See also Next-generation sequencing in clinical virology
Download Yes movies App to watch free movies online




Well explained
There is noticeably a bundle to learn about this. I assume you made certain nice points in options also.
A lot of what you assert happens to be astonishingly legitimate and it makes me ponder why I had not looked at this in this light previously. This piece truly did switch the light on for me personally as far as this subject matter goes. Nevertheless at this time there is one particular point I am not really too comfortable with and whilst I make an effort to reconcile that with the main theme of the position, let me see just what the rest of the subscribers have to say.Very well done.
what kind of sugar is put on cbd gummy bears